Are All Disjoint Sets Created Equal? Exploring Set Differences
What Are Disjoint Sets? | Set Theory
Keywords searched by users: Are all disjoint sets equal Pairwise disjoint, Disjoint Set, Empty set, Power set, if a = {10,15,20} then {10} ∈ a., Subset of a set, Disjoint union, Set algebra
Are Disjoint Sets Equal?
Understanding the Relationship Between Disjoint Sets, Equal Sets, and Equivalent Sets
In the realm of set theory, it’s important to clarify the distinctions between equal sets, equivalent sets, and disjoint sets. Equal sets are those in which every element of one set can be found in the other, and vice versa; they are essentially identical. However, equivalent sets, while related, don’t share this identical characteristic. Two sets can be considered equivalent if they have the same cardinality, meaning they contain the same number of elements, but they may not necessarily contain the same elements themselves.
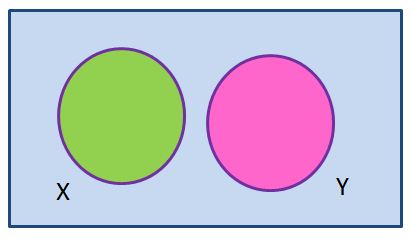
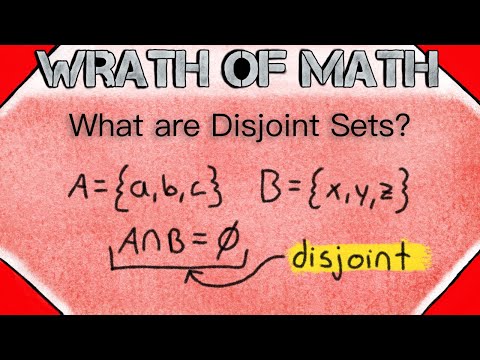
Now, let’s delve into the concept of disjoint sets. Two sets, A and B, are said to be disjoint when they have no elements in common whatsoever. This means that if you were to compare the elements of sets A and B, you wouldn’t find a single element that appears in both sets. In other words, their intersection is an empty set. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when working with sets in mathematics and various other fields, as it allows us to classify and compare sets based on their inherent properties and relationships.
What Are The Rules For Disjoint Sets?
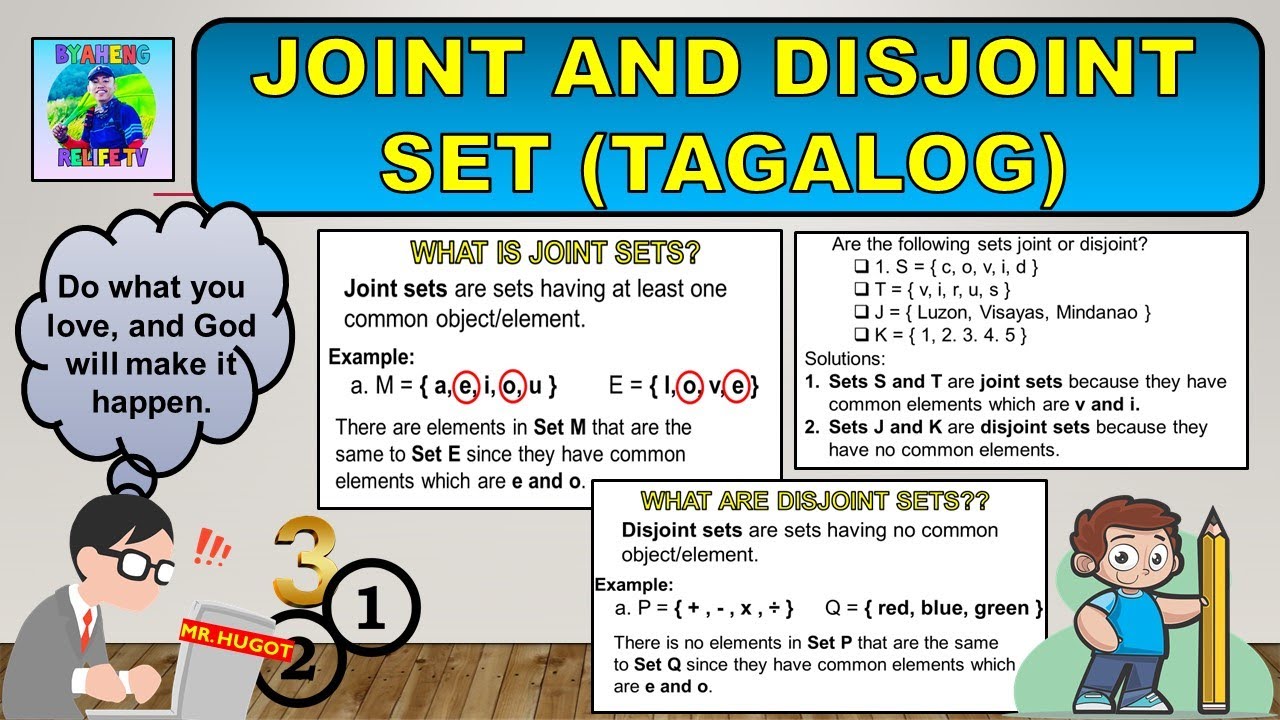
Disjoint sets, a concept frequently employed in mathematics, refer to sets that share no common elements. In other words, when you compare two sets, if there is no element they both contain, they are considered disjoint. Another way to express this is to say that the intersection of two disjoint sets results in the empty set, meaning there are no elements shared between them. For instance, let’s consider the sets {1, 2, 3} and {4, 5, 6}. Since there are no common elements between them, these sets are considered disjoint. On the contrary, when we examine {1, 2, 3} and {3, 4, 5}, we find that they share the element ‘3,’ making them not disjoint. Therefore, the presence or absence of shared elements is a fundamental aspect in determining whether sets are disjoint or not.
What If A And B Are Disjoint Sets?
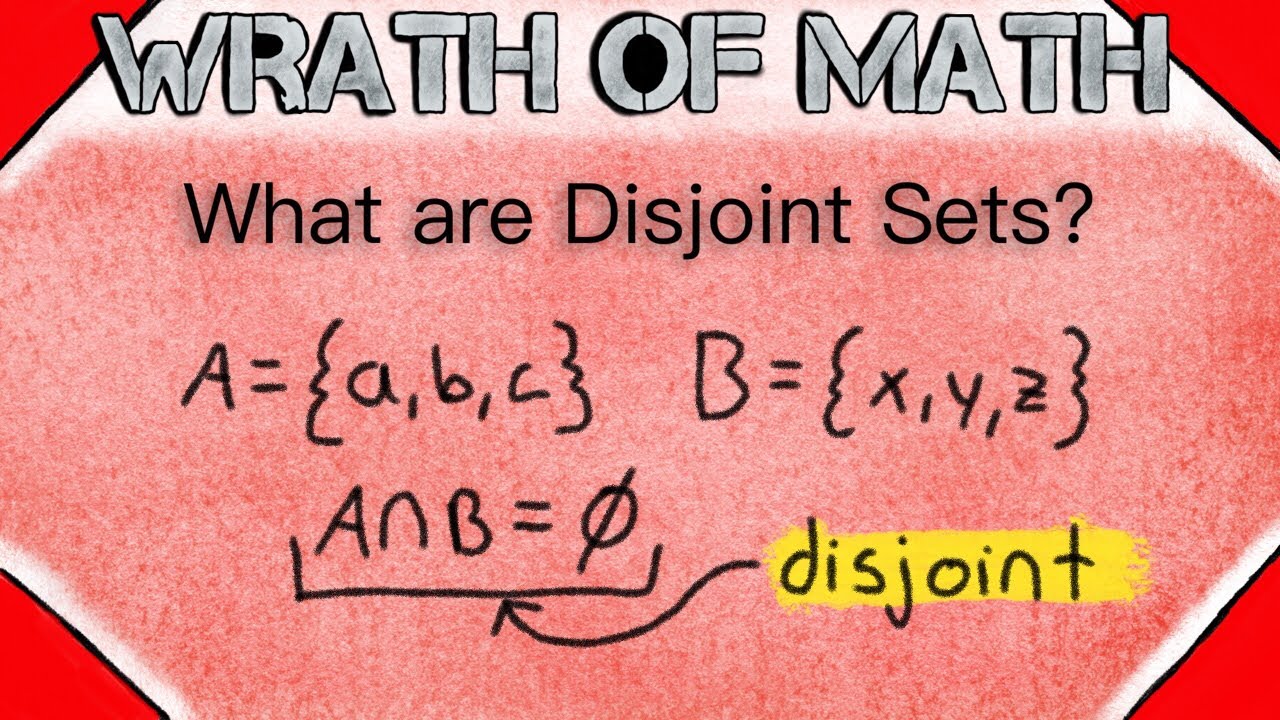
What if A and B are disjoint sets? When A and B are disjoint sets, it means that there is no overlap or commonality between the elements of these two sets. In such cases, the intersection of sets A and B, denoted as A∩B, will result in an empty set, represented as φ or {}. This implies that there are no shared elements between A and B, making them entirely distinct from each other. Disjoint sets play a fundamental role in set theory and various mathematical and analytical applications, as they help distinguish and analyze the relationships between different sets with no common elements.
Update 5 Are all disjoint sets equal



Categories: Update 66 Are All Disjoint Sets Equal
See more here: buoitutrung.com
Learn more about the topic Are all disjoint sets equal.
- Disjoint sets
- Pairs of Sets | Disjoint Sets | Overlapping Sets | Equivalent Sets
- Disjoint sets – Wikipedia
- Two sets A,B are disjoint if | Maths Questions – Toppr
- State whether each of the following statement is true or false. Justify …
- Definition & Examples | Pairwise Disjoint Set – BYJU’S
See more: https://buoitutrung.com/tech blog